The cryptocurrency revolution is unfolding unevenly across the globe, with developing nations emerging as unlikely champions in digital asset adoption. India holds the top spot globally with 97.5 million crypto owners (7.1% of population), while Nigeria ranks second with 22 million owners (10.3% of population). This phenomenon reveals how economic necessity, technological innovation, and demographic advantages have converged to make these countries global leaders in grassroots cryptocurrency adoption.
Understanding Global Crypto Adoption Leadership
According to the Chainalysis 2024 Global Crypto Adoption Index, India leads the world in cryptocurrency adoption for the second consecutive year, followed by Nigeria in second place. This ranking considers four key metrics: centralized service usage, retail centralized service usage, DeFi protocol engagement, and retail DeFi activity, all weighted by purchasing power parity and GDP per capita.
The dominance of lower-middle-income (LMI) countries in crypto adoption represents a fundamental shift from traditional financial technology adoption patterns. Forty percent of the world's population lives in LMI countries, and these nations have shown the strongest recovery in grassroots crypto adoption over the past year. This demographic represents the future of global economic growth, making their crypto adoption patterns particularly significant for the industry's trajectory.
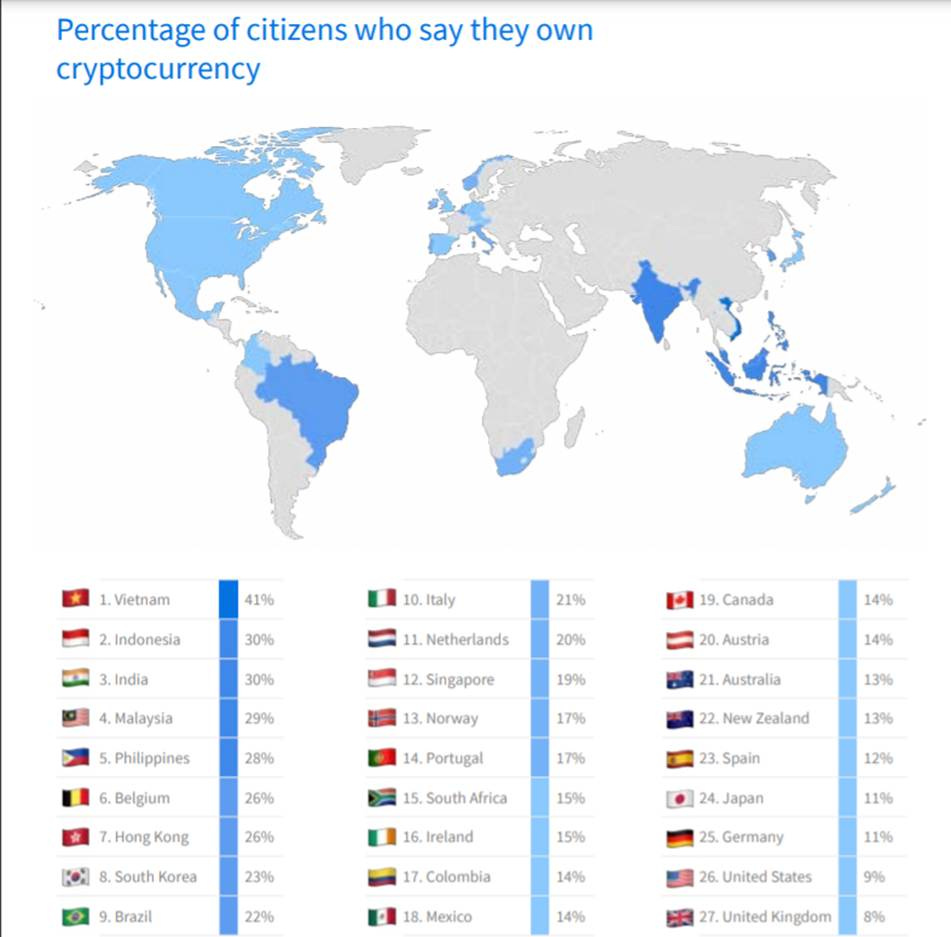
World map showing percentage of citizens who own cryptocurrency by country, highlighting Vietnam, India, and Indonesia among top adopters.
India: The World's Crypto Capital
Demographic and Technological Advantages
India's position as the global crypto leader stems from several converging factors. The country benefits from a massive tech-savvy youth population, widespread mobile internet adoption, and significant interest in alternative investment opportunities. With 190 million Indians remaining unbanked, cryptocurrencies provide essential financial services to those excluded from traditional banking systems.
The demographic composition of Indian crypto users reflects this technological embrace. Female crypto users in India grew by 300% between 2020 and 2021, while 66% of users on India's largest exchange WazirX are under 35 years old. This young user base, combined with high digital literacy and widespread mobile internet usage, creates an ideal environment for crypto adoption.
Economic and Regulatory Drivers
Despite facing regulatory challenges, including a 30% capital gains tax and 1% tax deducted at source (TDS) on transactions, India's crypto market continues to thrive. The country's approach has evolved from outright hostility to cautious acceptance, with crypto adoption flourishing even amid regulatory uncertainty.
India's crypto adoption is driven by factors such as huge unbanked population and high mobile penetration. The country's vibrant Web3 ecosystem, including major players like Polygon and CoinSwitch Kuber, has attracted significant investment and driven innovation. Additionally, Gen Z prefers high-risk/high-reward financial instruments like cryptocurrencies, while millennials favor more secure investment avenues.
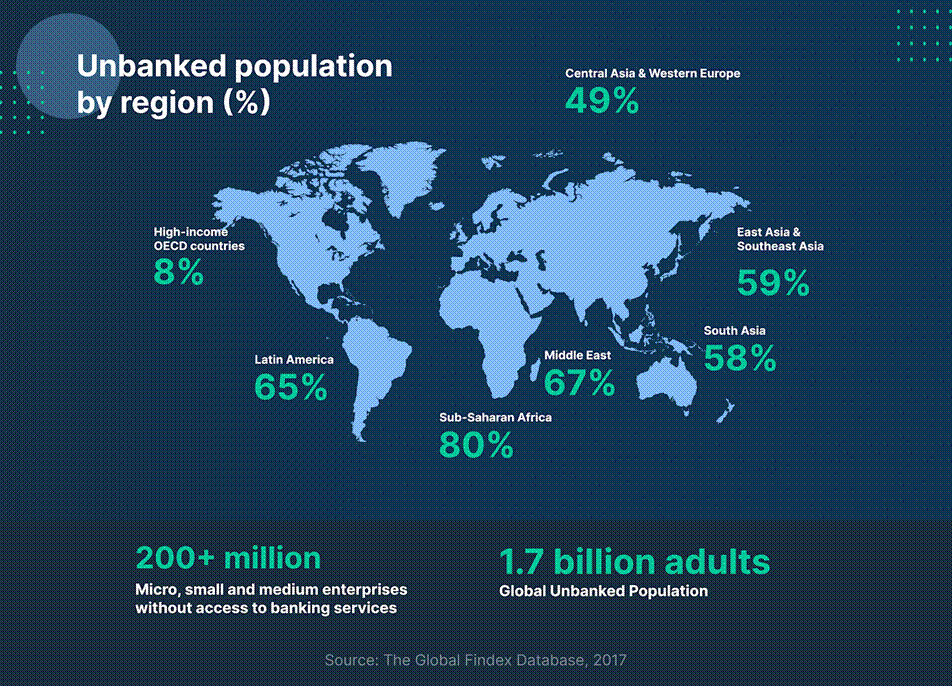
Unbanked population percentages by region highlight financial exclusion challenges worldwide, providing context for cryptocurrency adoption in emerging markets.
Nigeria: Africa's Crypto Pioneer
Economic Necessity Driving Adoption
Nigeria's second-place ranking reflects the country's use of cryptocurrency as a practical solution to systemic economic challenges. With inflation reaching over 24% in 2023 and the naira losing more than three-quarters of its value against the US dollar since 2016, Nigerians have turned to digital assets for financial stability.
The scale of Nigeria's crypto adoption is remarkable. Between July 2023 and June 2024, Nigeria processed approximately $59 billion in cryptocurrency transaction value, with 85% of transactions valued under $1 million, signaling strong retail participation. This grassroots adoption pattern distinguishes Nigeria from markets driven primarily by institutional activity.
Peer-to-Peer Trading and Stablecoins
Nigeria's crypto ecosystem is characterized by innovative peer-to-peer (P2P) trading networks. P2P platforms like Paxful and Binance P2P allow users to exchange naira for crypto directly with one another, bypassing the commercial banking system. This infrastructure has proven resilient despite regulatory restrictions, with users adapting through alternative channels like WhatsApp and Telegram groups.
Stablecoins have become particularly important in Nigeria, accounting for 43% of retail transactions under one million dollars as Nigerians hedge against naira instability. These dollar-pegged digital assets offer a way to preserve purchasing power in an environment of persistent currency devaluation and high inflation.
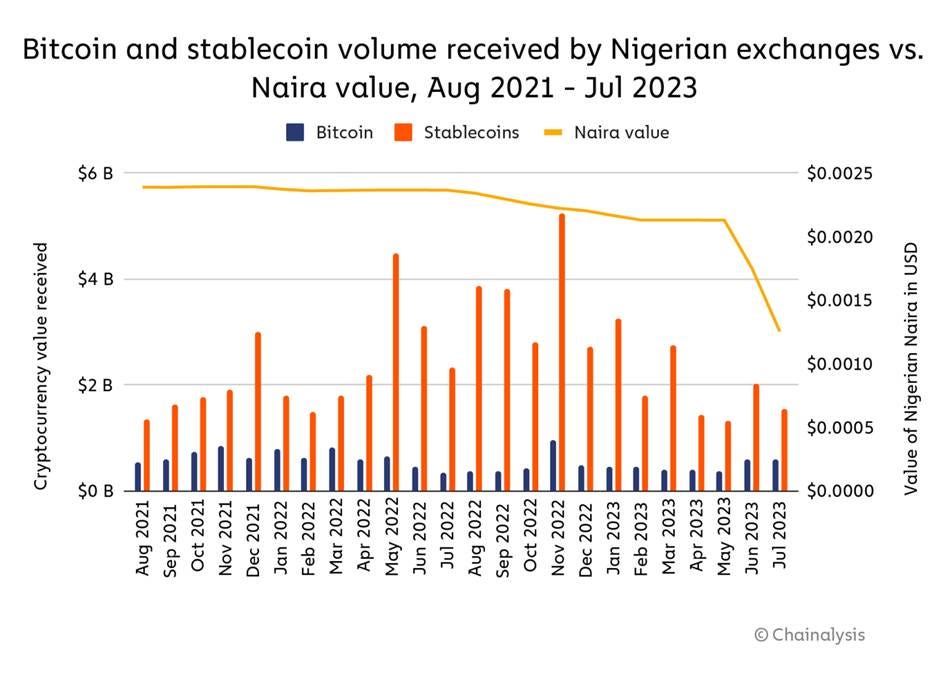
Bitcoin and stablecoin volumes received by Nigerian exchanges compared to the Nigerian Naira value from August 2021 to July 2023, showing stablecoin dominance and currency value decline.
The Economic Foundation of Crypto Adoption
Inflation Hedge and Currency Diversification
The appeal of cryptocurrencies in developing nations stems largely from their function as an inflation hedge and alternative store of value. Countries with high inflation rates and currency devaluation see increased cryptocurrency adoption as citizens seek to protect their wealth from rapidly devaluing local currencies.
This pattern extends beyond India and Nigeria. Venezuela ranks 13th globally for crypto adoption with a 110% increase in usage, while citizens use stablecoins to protect against hyperinflation that reached 229% in May 2025. Similarly, Argentina, Turkey, and other countries experiencing economic instability have seen surge in crypto usage as alternative financial tools.
Remittances and Cross-Border Payments
Cryptocurrency adoption in developing countries is strongly tied to remittance flows. Nigeria receives more than $20 billion worth of remittances annually, with traditional transfer services charging fees as high as 36% for every $200 sent from overseas. Cryptocurrencies offer a faster, cheaper alternative, with crypto exchanges typically charging a fraction of traditional remittance costs.
The World Bank estimates that nearly $550 billion worth of remittances were sent to low- and middle-income countries in 2019, with crypto offering secure and fast cross-border transactions. This use case is particularly relevant in countries like the Philippines, where remittances account for significant portions of GDP.
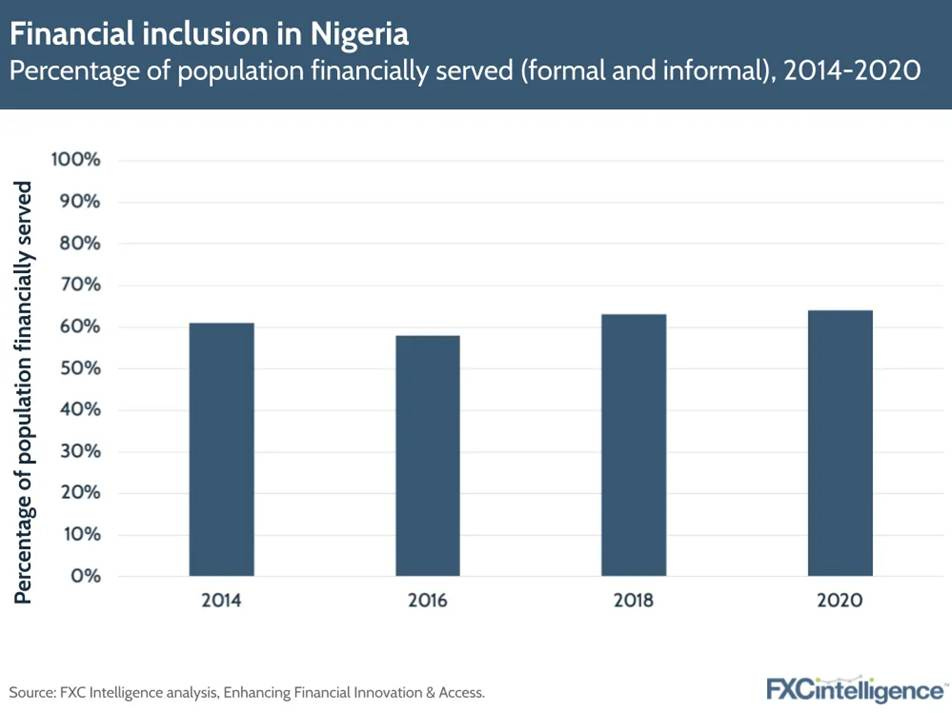
Financial inclusion in Nigeria increased from 58% to 64% of the population between 2014 and 2020, indicating growing access to financial services.
Financial Inclusion: The Digital Banking Revolution
Mobile-First Financial Services
The rise of mobile payment services has created fertile ground for cryptocurrency adoption in developing nations. In Sub-Saharan Africa, the region is home to nearly half of the world's 1.04 billion registered mobile money accounts. This mobile-first financial infrastructure provides the technological foundation necessary for crypto adoption.
Nigeria's financial inclusion has gradually increased from 61% in 2014 to 64% in 2020, but significant gaps remain. Cryptocurrencies fill these gaps by providing permissionless financial services that require only a smartphone and internet connection. This accessibility is crucial in regions where approximately 36% of Nigerian adults remain unbanked.
Technological Infrastructure and Innovation
The technological readiness of developing nations plays a crucial role in crypto adoption. Countries with robust internet penetration, advanced mobile networks, and high rates of digital literacy are more likely to see higher cryptocurrency adoption rates. This infrastructure enables the development of local crypto exchanges, mobile wallet services, and peer-to-peer trading networks.
India and Nigeria both benefit from strong technological ecosystems that support crypto innovation. India's position as a global technology hub provides the technical expertise necessary for crypto development, while Nigeria's fintech sector has experienced rapid growth, with companies like Moniepoint achieving billion-dollar valuations.
Regulatory Environment and Adaptation
Evolving Government Approaches
The relationship between governments and cryptocurrency adoption in developing nations has been complex and evolving. Nigeria underwent a significant regulatory turnaround, lifting crypto restrictions in December 2023 after banning crypto in 2021. This shift reflects growing recognition that prohibition is ineffective in curbing adoption when economic necessity drives usage.
India's approach has similarly evolved from hostility to cautious acceptance, with the government implementing high taxes rather than outright bans. Despite these challenges, crypto adoption continues to rise as users find ways to navigate regulatory constraints.
Innovation Despite Restrictions
Remarkably, crypto adoption has often thrived despite regulatory challenges. Venezuela's crypto ecosystem remains resilient despite government crackdowns, with citizens creating parallel financial systems using digital assets. This resilience demonstrates how economic necessity can drive innovation and adoption even in hostile regulatory environments.
The adaptability of crypto users in developing nations has led to innovative solutions. Nigerian crypto users found ways to continue trading using WhatsApp and Telegram groups after traditional banking restrictions. Similarly, Venezuelan businesses and universities have embraced blockchain education and crypto payment systems despite government uncertainty.
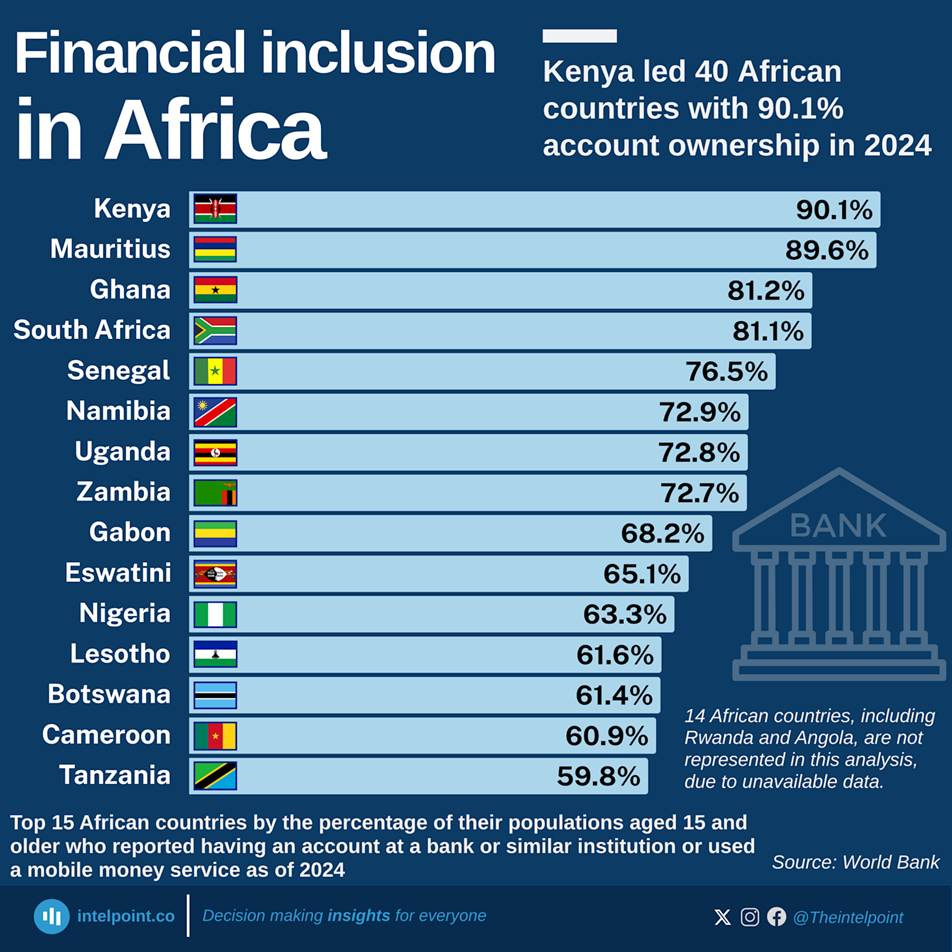
Top 15 African countries by financial inclusion rate in 2024, led by Kenya with 90.1% account ownership.
Market Dynamics and Future Trends
Lower-Middle Income Country Leadership
The concentration of crypto adoption in lower-middle-income countries represents a significant trend in global financial technology adoption. LMI countries have seen the greatest recovery in grassroots crypto adoption and are the only category whose total adoption remains above pre-2020 levels. This pattern suggests that crypto adoption will continue to be driven by emerging markets rather than developed economies.
The 2024 data shows crypto activity increased across countries of all income brackets, but LMI countries maintained their leadership position. This trend is particularly significant given that 40% of the world's population lives in LMI countries, making their adoption patterns crucial for the industry's future growth.
Institutional vs. Grassroots Adoption
While developed countries like the United States see crypto adoption driven primarily by institutional investors, developing nations are characterized by grassroots, retail-driven adoption. Nigeria's crypto activity is largely driven by smaller denomination retail transactions, with around 85% of transfers under $1 million.
This grassroots adoption pattern creates different market dynamics and use cases. Rather than speculative investment, crypto serves practical purposes in developing nations: remittances, inflation hedging, and access to financial services. These real-world applications provide a more stable foundation for long-term adoption.
The Social and Economic Impact
Youth Demographics and Digital Nativity
The demographic composition of crypto users in leading adoption countries reveals important trends. In Nigeria, 35% of adults are crypto investors, with more than 52% of them under 30 years old. This young user base is digitally native and more willing to experiment with new financial technologies.
In India, the 25-34 age group makes up 31% of crypto users globally, while Gen Z accounts for 28% of global crypto participants. This demographic shift suggests that crypto adoption will continue to grow as these digital natives reach peak earning years and gain greater financial resources.
Gender Dynamics in Crypto Adoption
While crypto adoption globally skews male, developing nations are seeing important changes in gender participation. Women account for 39% of global crypto owners, with significant growth in female participation in countries like India. This broader participation base strengthens the foundation for sustained adoption growth.
The gender gap varies by region and age group, with younger demographics showing more balanced participation. As financial inclusion efforts target underserved populations, including women, crypto adoption patterns are likely to become more diverse and inclusive.
Financial inclusion in Kenya increased significantly from 2006 to 2021 as formal financial access rose sharply, while informal access and exclusion declined.
Challenges and Opportunities
Infrastructure and Connectivity Barriers
Despite rapid growth, crypto adoption in developing nations faces significant challenges. Connectivity issues hinder widespread crypto use in countries like Venezuela, while access limitations affect adoption potential. Additionally, many developing economies lack the technological infrastructure needed for widespread crypto adoption.
Educational barriers remain significant, with low financial literacy acting as a key deterrent to crypto adoption. Addressing these challenges requires coordinated efforts from governments, educational institutions, and the crypto industry to build awareness and infrastructure.
Regulatory Uncertainty and Risk
The regulatory environment in many developing countries remains uncertain, creating both opportunities and risks. Regulatory uncertainty is cited as a major barrier limiting corporate adoption of cryptocurrencies in India. Similarly, the absence of clear regulatory frameworks in various countries creates challenges for both users and service providers.
However, some countries are making progress. Brazil's regulatory evolution and pro-innovation policies have increased regulatory certainty and attracted major crypto players like Circle. This demonstrates how balanced regulatory approaches can support adoption while managing risks.
Conclusion: The Future of Global Crypto Adoption
The leadership of India and Nigeria in global cryptocurrency adoption reflects a fundamental shift in how financial innovation spreads globally. Unlike previous technological revolutions that originated in developed countries and gradually spread to emerging markets, the cryptocurrency revolution is being driven by necessity and innovation in developing nations.
The concentration of crypto adoption in lower-middle-income countries, where 40% of the world's population lives, suggests that crypto's future will be shaped by these markets rather than traditional financial centers. The practical use cases that drive adoption in these countries—remittances, inflation hedging, and financial inclusion—provide a more sustainable foundation than speculative investment.
As infrastructure improves, regulatory frameworks mature, and digital literacy expands, the leadership of countries like India and Nigeria in crypto adoption is likely to strengthen further. Their success demonstrates that when economic necessity meets technological opportunity, innovation can flourish even in challenging regulatory and economic environments.
The global crypto adoption patterns we see today may well define the future of international finance, with developing nations leading the transition to a more inclusive, decentralized global financial system. Understanding these patterns is crucial for policymakers, investors, and technology developers seeking to participate in this transformation.
Notes: This is my own opinion and not the opinion of my employer, State Street, or any other organization. This is not a solicitation to buy or sell any cryptocurrency or stock. I use a Large Language Model (LLM) aided workflow. This allows me to test 5-10 ideas and curate the best 2-4 a week for you to read. We are always seeking feedback to enhance this process.
Additionally, if you would like updates more frequently, follow me on X:https://x.com/cryptowalk2000. In addition, feel free to send me corrections, new ideas for articles, or anything else you think I would like: cameronfen at gmail dot com.
Source:
1. https://coinledger.io/research/top-10-countries-that-use-bitcoin
2. https://breet.io/blog/crypto-and-bitcoin-adoption-statistics-in-nigeria
4. https://admin.lexikon.com.mx/archivos/The_2024_geography_of_crypto_report_1729164229.pdf
5. https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/2024-global-crypto-adoption-index/
6. https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/2023-global-crypto-adoption-index/
9. https://graphlinq.io/blog-posts/top-10-countries-and-governments-holding-the-most-cryptocurrency
10. https://www.ijfmr.com/research-paper.php?id=51153
11. http://www.emerald.com/bl/article/37/1/27-44/1219824
12. https://www.bitpace.com/blog/5-reasons-india-is-a-leader-in-global-crypto-activity/
13. https://blockworks.co/news/chainalysis-global-adoption-index-india-lmi
14. https://www.ijfmr.com/research-paper.php?id=43215
15. https://business.cornell.edu/article/2025/08/grassroots-cryptocurrency-adoption/
17. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/Delivery.cfm/5193998.pdf?abstractid=5193998&mirid=1
18. https://www.bitira.com/crypto-global-adoption/
19. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/17530350.2024.2413111
20. https://cointelegraph.com/news/venezuela-crypto-adoption-bolivar-inflation-2025
22. https://cryptoforinnovation.org/crypto-in-nigeria-surge-in-adoption-and-regulatory-shifts/
23. https://www.bitstamp.net/learn/crypto-101/cryptocurrency-adoption-in-developing-countries/
25. https://101blockchains.com/cryptocurrency-adoption-in-developing-nations/
26. https://research.tees.ac.uk/files/92823246/92609466.pdf
27. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/top-3-crypto-action-stories-may-nigeria-qaehe
29. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/Delivery.cfm/5091641.pdf?abstractid=5091641&mirid=1
30. https://coinlaw.io/crypto-user-demographics-statistics/
31. https://coinledger.io/research/how-many-people-own-crypto-in-the-world
33. https://ijsrem.com/download/regulatory-challenges-of-cryptocurrency-adoption-in-corporate-finance/
Picture Sources:
1. https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/subsaharan-africa-crypto-adoption-2024/
2. https://www.cryptohopper.com/news/the-importance-of-p2p-trading-in-emerging-markets-9468
3. https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/africa-cryptocurrency-adoption/
5. https://financeinafrica.com/insights/cash-digital-banked-african-countries/